Ectopic gene expression is an important tool for gene analysis and protein science, offering insight into gene function at multiple levels. Gain-of-function experiments often result in phenotypic changes which can provide the counterpart to loss-of-function studies, such as gene knockdown.
Gene expression constructs, such as cDNAs and ORFs, are commonly used to over-express a protein of interest to be analyzed for effect on cellular phenotype, intracellular localization, or for the isolation and purification of a protein for further study.
This schematic demonstrates a gene expression construct being translated and expressed in a eukaryotic cell. Once in the nucleus, the cellular machinery recognizes the promoter, transcribes the protein coding sequence into mRNA and translates the protein. The resulting gene product can cause alterations in phenotype, be purified for further processing or to be tracked via localization to better understand protein function.
Gene expression tools
Complementary DNA (cDNA) and open reading frames (ORF) are two tools derived from native mRNA that can facilitate gene expression and over-expression assays.
- cDNA is derived from mRNA and contain the ORF as well as all or part of the 5' and 3' untranslated regions, to more closely mimic the context of native regulation.
- ORFs are created from cDNA by removing the untranslated regions leaving just the protein coding open reading frame, providing a shortcut to protein expression.
Pre-cloned cDNAs and ORFs reduce the amount of time needed to clone or synthesize a gene of interest, allowing researchers to spend more time analyzing the results of their over-expression experiment, and less time creating the expression construct itself.
Endogenous gene expression with CRISPRa
CRISPR activation (CRISPRa) is a new method of gene overexpression that harnesses the cell's native machinery to upregulate target endogenous gene expression levels by up to 10,000x. Learn more about CRISPRa.
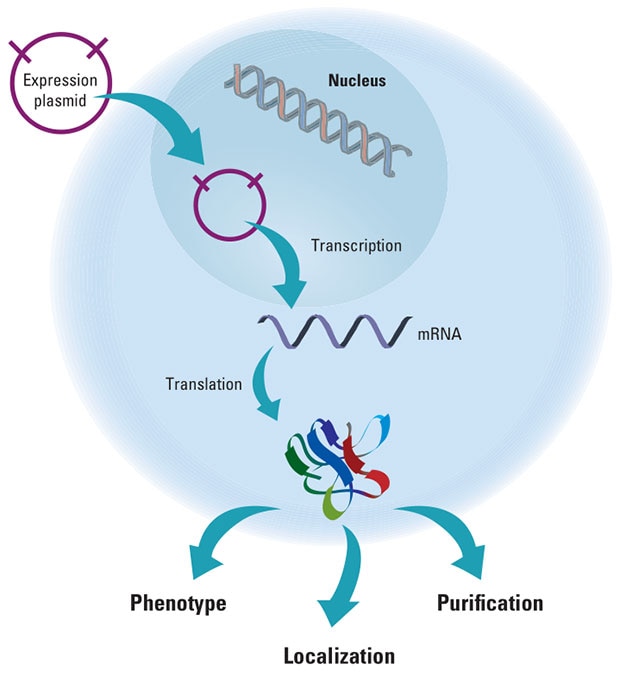
Gene Expression Pathway
This schematic demonstrates a gene expression construct being translated and expressed in a eukaryotic cell.Gene Expression Pathway
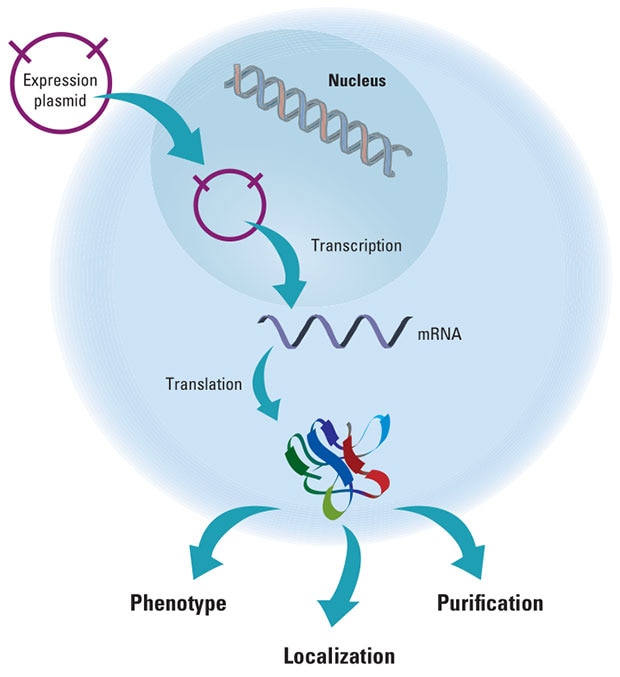
This schematic demonstrates a gene expression construct being translated and expressed in a eukaryotic cell.
Order Products
Gene Expression (cDNAs and ORFs)
cDNAs and ORFs can be used to overexpress particular genes of interest. Choose from individual clones, lentiviral ORFs, and genome-scale libraries.
Mammalian cDNAs
Derived from mRNA and including 5’ and 3’ UTRs, our cDNA collections are ideal for overexpressing a gene in the context of native regulation.
Mammalian ORFs
With both 5’ and 3’ UTRs removed, open reading frames (ORFs) provide a shortcut to protein expression.
Non-Mammalian cDNAs and ORFs
Your complete source for cDNAs, ORFs, knockout strains, promoter collections and other resources for yeast, C. elegans, Zebrafish, Xenopus, and E. coli.
Helpful Resources
cDNA Clones and Plates - Technical Manual
Dharmacon cDNA Clones
Top five considerations for ORF selection
This list presents the major considerations to help you quickly and effortlessly select the right clone(s) for your over-expression project
